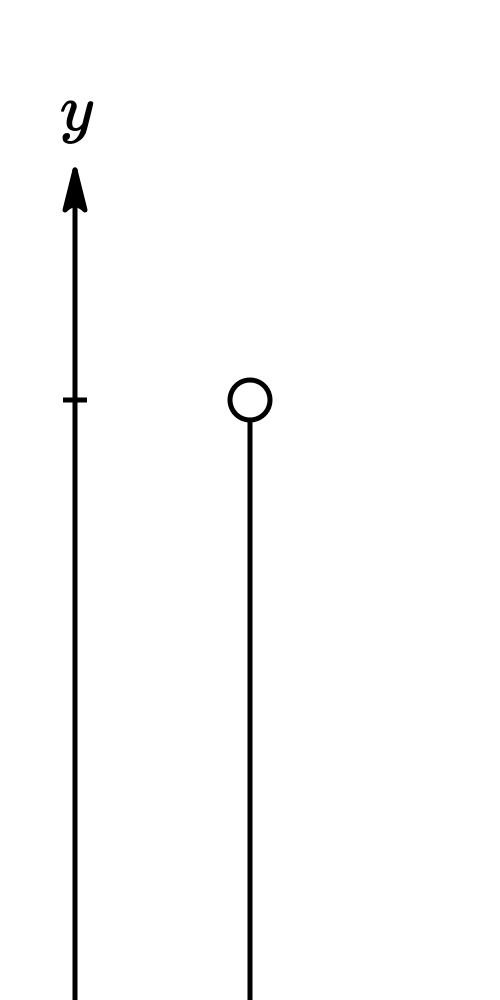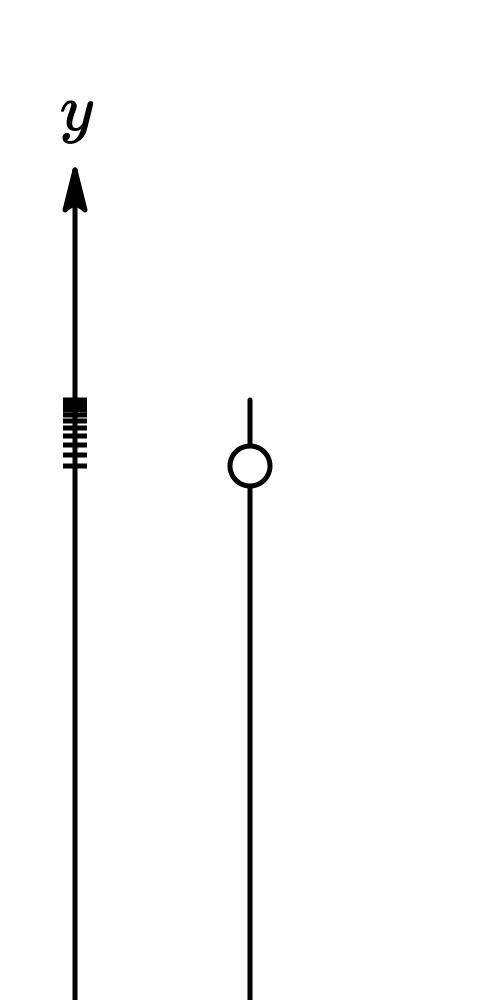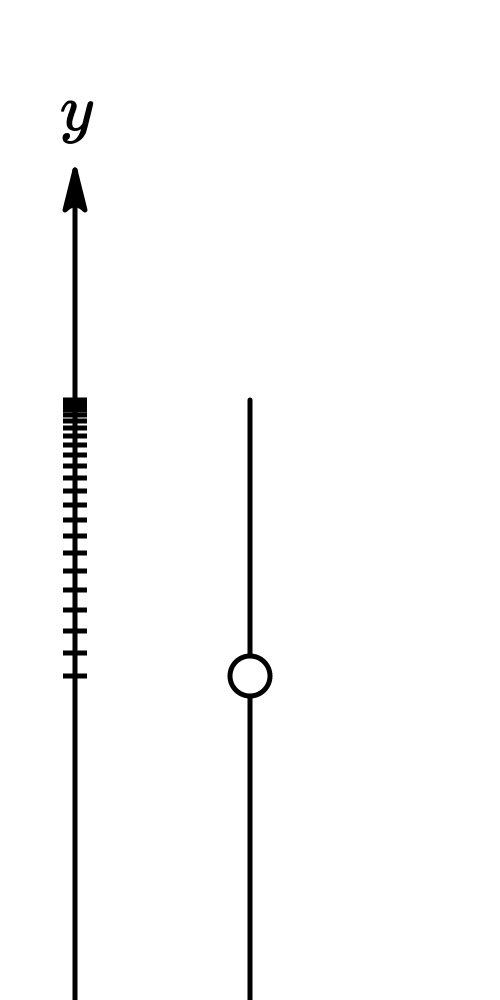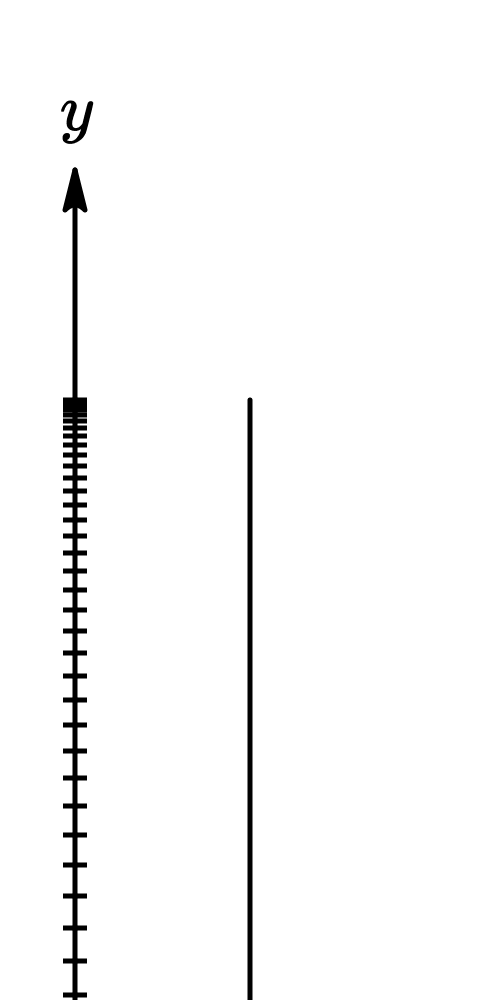
A freely falling object is an object that moves under the influence of gravity only.
An objects experience free fall when there is no air resistance or when air resistance is negligible.
Free fall is the motion of a object where its weight is the only force acting on an object.
If neglecting air resistance (and friction), all objects in free fall in the earth's gravitational field have a constant acceleration, independent of mass, which is directed towards the earth's center (or perpendiculr to the earth's surface) and of magnitude $|\underset{a}{\rightarrow}|$ ≡ $g$ = 9.8$/s^2$.
There are two important motion characteristics that are true of free - falling objects:
- Free - falling objects do not encounter air resistance (and friction).
- All free - falling objects accelerate downwards at a rate of $9.8 m/s^2$.
Example: If we drop a feather and a piece of rock in a tube, the rock will accelerate faster and get into the ground faster (Because, of air resistance). But if we put the feather and rock in a evacuated (removed the air) tube, both will have the same acceleration, and both get into the ground at a same time.
Equation
of Motion in Straight Line
|
Equation
of motion under gravity
|
For
downward motion
|
For
upward motion
|
$v = u + at$
|
$v= u +gt$
|
$v= u - gt$
|
$s = ut + \frac{1}{2} at^2$
|
$s = ut + \frac{1}{2} gt^2$
|
$s = ut - \frac{1}{2} gt^2$
|
$v^2 + u^2 = 2as$
|
$v^2 + u^2 = 2gs$
|
$v^2 + u^2 = - 2gs$
|